https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1I1vxu5qIUM
Transmit an electromagnetic wave (binary) with different wavelength
eg: 121mm = 1 124mm = 0
the waves send in all directions
Bluetooth range: 2.4835GHz - 2.4GHz
Divided in different sections (79 channels), each section has a pair of wavelengths representing 0 and 1
the bluetooth range is shared with some other device like a microwave oven
like the power of a microwave oven is too large for bluetooth.
it may destroy the bluetooth device if you put them inside the microwave oven (danger)
Data Integrity#
Packet#
- Access Codes (72 bits)
- Header (54bits)
- Payload (vary, depends on the function)
Frequency Hopping#
Two bluetooth devices will have a set of channels to send data
They will change the channels frequently
Error Detection#
Noise Filtering#
Data Transmit#
Frequency Shift Keying#
carrier wave adjusts the wavelength to send 0 and 1
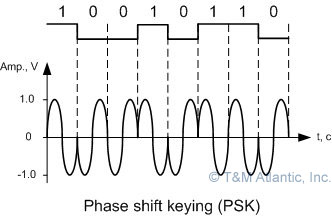
Phase Shift Keying#
constant wavelength and attitude
use the wave function to determine 0 and 1 (like sin x = 0, cos x = 1, instead of A sin x and B sin X)